Laser heat treatment
- Introduction to Laser Heat
Treatment Technology - Comparison of laser heat treatment
and induction heat treatment - Laser heat treatment equipment
and technical manpower - Laser Heat
Treatment Features - Process reduction
and cost reduction
Comparison between Laser Heat Treatment-Applied Products and High-Frequency Heat Treatment-Applied Products
Principles of Laser Heat Treatment
Laser heat treatment is a heat treatment that can perform heat treatment while minimizing the heat effect in the state of the completed finish machining of precision parts which is difficult to do with conventional surface heat treatment, thereby shortening post-process and reducing total costs through the minimization of deformation amount. Super-fast heating and self-cooling can form ultra-fine and full martensite, providing excellent wear resistance. In addition, it consumes less energy than conventional surface heat treatment and does not require a coolant, so it is an eco-friendly heat treatment suitable for carbon neutrality. Any area that can irradiate the laser beam can be heat-treated on products that were not possible in the existing heat treatment technologies, such as partial quenching of precision products or parts with complex shapes.
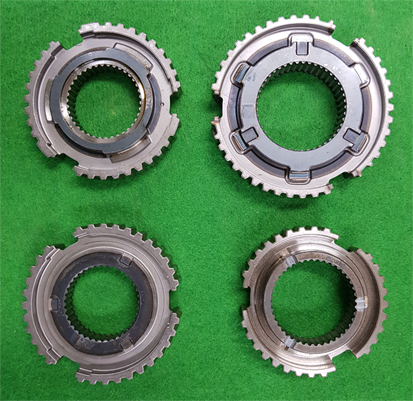
Applied Products
Laser heat treatment is a local heat treatment that can selectively harden only areas that receive a lot of load, and materials with a carbon content of 0.3% or more, such as carbon alloy steel and cast iron, are suitable for such treatment. For example, in the case of automobile press molds or injection molds, high heat is irradiated to areas that receive a lot of surface load, such as corners and edges, to transform the structure and increase the hardness. In general, case depth is less than 1mm, and the laser heat treatment can be applied to complex shapes or products such as various gears, shaft types, camshafts, cutting tools, and guide rails.
Comparison with High-Frequency Heat Treatment, which Is a Similar Heat Treatment
 |
Deformation amount
The most similar heat treatment to laser heat treatment is high-frequency heat treatment. Because high-frequency heat treatment is also a local heat treatment, deformation is small compared to other full-hardening heat treatments, but compared to laser heat treatment, the amount of deformation is larger because the heat effect is large.
|
 |
Hardness
Because laser heat treatment has a fast heat input and cooling rate, it is easy to obtain relatively high hardness even with low-cost carbon steel for mechanical structure, and it is easy to obtain hardness similar to or higher than that of high-frequency heat treatment.
|
 |
Case Depth
Laser heat treatment: 1mm or less, easy to control depth in 0.1mm increments
High-frequency heat treatment: 1mm or more, difficult to control depth in 0.1mm increments |
 |
Heat Treatment Range
Laser heat treatment: It is possible to heat treatment in an exceedingly small range and complex shapes that can be reached by the laser beam, but it is difficult for a large area
High-frequency heat treatment: Large area partial heat treatment is possible, but heat treatment in an exceedingly small range and complex shape is difficult |
 |
Cost and Process Time
Laser heat treatment costs are determined by the surface area and size of the operation. Although the unit price per hour of laser heat treatment is higher than that of high-frequency heat treatment, the machining time is shorter depending on products, and the cost reduction potential is higher as the process shortens due to low deformation and the coil cost and manufacturing time are unnecessary. However, heat treatment of a large area requires a long machining time due to the limitation of the laser beam size.
|
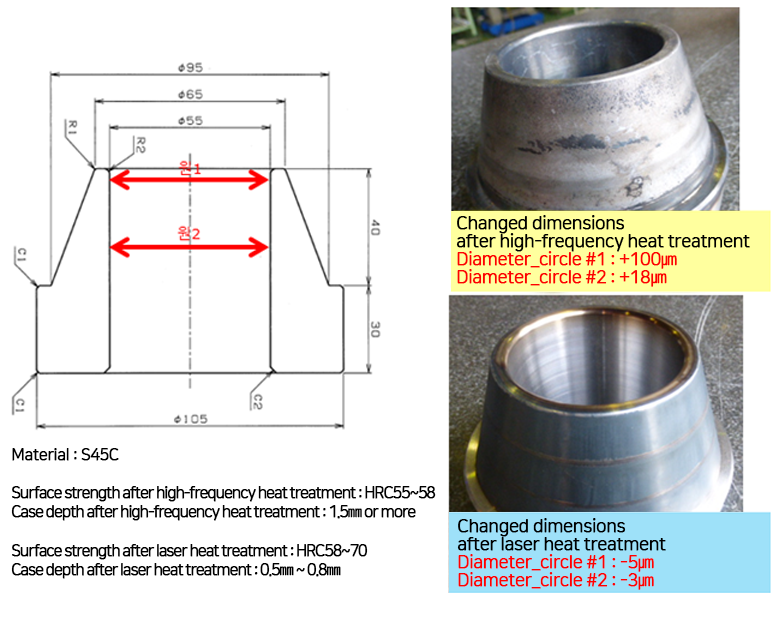
Comparison of Deformation Amount between High-Frequency Heat Treatment and Laser Heat Treatment
The figure below is an example of a product called taper cone, which requests that the taper surface be heat-treated. The dimensions were respectively measured after high-frequency heat treatment and laser heat treatment. As for the measurement method, the inner diameter size of circle 1 and circle 2 in the drawing was measured.
| Deformation amount caused by high-frequency heat treatment | Deformation amount caused by laser heat treatment |
|---|---|
| After high-frequency heat treatment, the size of circle 1 became + 100 microns. The size of circle 2 was + 18 microns, and the tapered surface was cracked open. |
After the laser heat treatment was performed, the size of circle 1 and circle 2 is -5 microns and -3 microns, respectively. In conclusion, this data shows that there is no problem even if laser heat treatment is performed after the finishing machining. Less deformation and warping after heat treatment is a characteristic of laser heat treatment. |

 Business
Business 


